Yes, You Still Need to Use Sunscreen
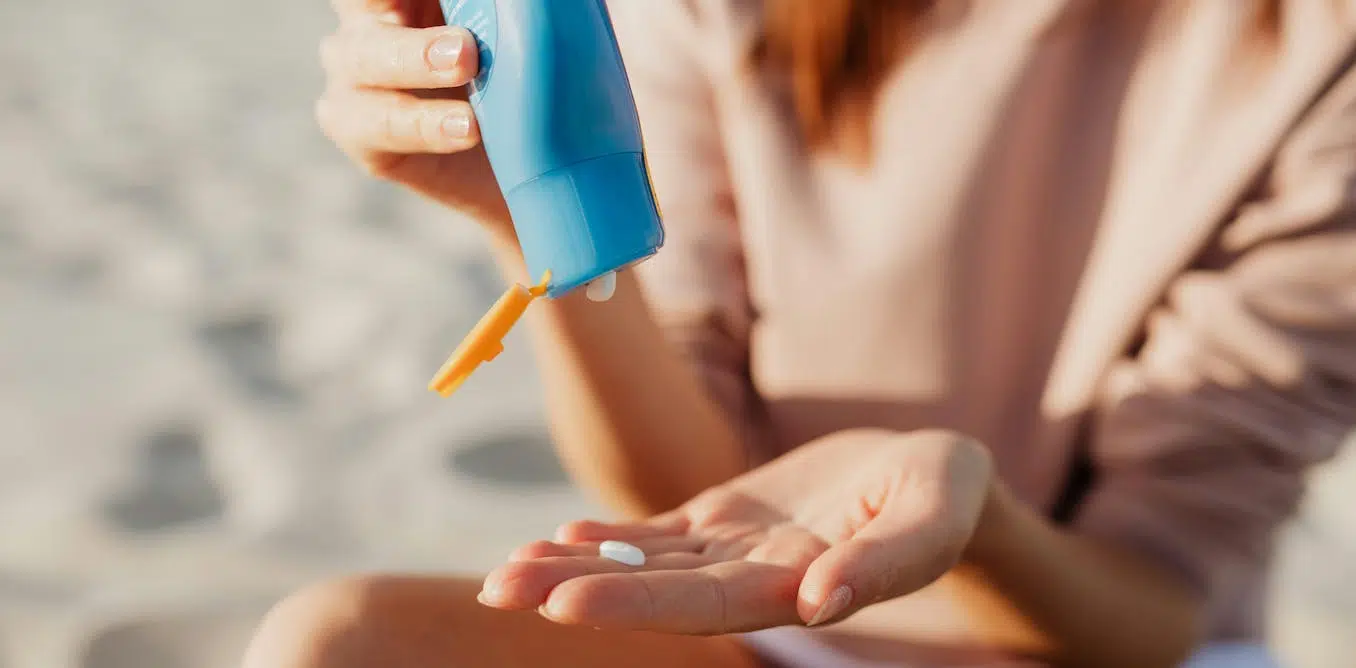

How Does Sunscreen Work and Is it Healthy to Go Sunscreen-Free?
How Does Sunscreen Work?
Because of Australia’s extreme UV environment, most people with pale to olive skin or other risk factors for skin cancer need to protect themselves. Applying sunscreen is a key method of protecting areas not easily covered by clothes.
Sunscreen works by absorbing or scattering UV rays before they can enter your skin and damage DNA or supportive structures such as collagen. When UV particles hit DNA, the excess energy can damage our DNA. This damage can be repaired, but if the cell divides before the mistake is fixed, it causes a mutation that can lead to skin cancers.
The Most Common Skin Cancers
The most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Melanoma is less common, but is the most likely to spread around the body; this process is called metastasis.
Sunscreen Can Help Prevent Skin Cancers
Used consistently, sunscreen reduces your risk of skin cancer and slows skin ageing. In a Queensland study, participants who used sunscreen daily for almost five years reduced their risk of squamous cell carcinoma by 40% compared to the other group. Ten years later, the daily use group had reduced their risk of invasive melanoma by 73%.
Does Sunscreen Block the Health-Promoting Properties of Sunlight?
The answer is a bit more complicated, and involves personalized risk versus benefit trade-offs. Sunscreen only filters UV rays, not visible light or infrared light (which we feel as heat). And importantly, some of the benefits of sunlight are obtained via the eyes.
Benefits of Exposing the Skin to UV Radiation
Exposing the skin to UV radiation produces vitamin D, which is critical for healthy bones and muscles. Vitamin D deficiency is surprisingly common among Australians, peaking in Victoria at 49% in winter and being lowest in Queensland at 6% in summer.
Conclusion
The balance of evidence suggests it’s better for people who are susceptible to skin cancer to continue with sun protection practices, with vitamin D supplementation if needed. There are some benefits of exposing the skin to UV radiation that might be blunted by sunscreen, but whether it’s worth foregoing those benefits to avoid skin cancer depends on how susceptible you are to skin cancer.
FAQs
Q: Is sunscreen necessary for people with darker skin that rarely or never burns?
A: No, if you have darker skin that rarely or never burns, you can go without daily sunscreen – although you will still need protection during extended times outdoors.
Q: Is it safe to go sunscreen-free if you’re not susceptible to skin cancer?
A: Yes, if you have darker skin or other factors that make you less susceptible to skin cancer, you can consider going without sunscreen. However, it’s still important to take precautions during extended times outdoors.
Q: What are the benefits of vitamin D?
A: Vitamin D is critical for healthy bones and muscles.
Q: Is it safe to take a vitamin D supplement?
A: Yes, vitamin D supplementation is safe and effective in preventing deficiency. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement.
Recent Posts
I Found Running Belts with Tons of Pockets That Actually Stay in Place
Best Streamlined: Lululemon Fast and Free Running Belt Stretchy zipper pocket, plus four smaller envelope…
13 Remedies to Soothe a Sore Throat
A Sore Throat Can Make You Feel Miserable 1. Warm Beverages Warm drinks, like teas…
Wellness Bodybuilder Wynter Addams’ Tips for Massive Quads
Wynter Addams Quad Training IFBB Pro League Wellness competitor Wynter Addams must focus on superior…
White snus: why ‘tobacco free’ doesn’t mean risk free
A Worrying Trend in Nicotine Use Among Teenagers and Professional Footballers A Growing Concern in…
How This 53-Year-Old Lost Fat, Built Strength, and Kept It Off (Without Starving)
Why Crash Dieting Fails (Especially Over 50) How Anthony Finally Lost Weight (And Kept It…
Everyday discrimination linked to increased anxiety and depression across all groups of Americans
Everyday Discrimination Linked to Higher Rates of Anxiety and Depression People who most frequently encounter…


