What to Know

How SNRIs Work and Their Uses
SNRIs (Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors) are a class of antidepressants that block the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine in the body. They are taken to treat depression, anxiety disorders, nerve pain, muscle pain, and fibromyalgia.
How SNRIs Work and Their Uses
SNRIs work to relieve the symptoms of various psychiatric disorders by inhibiting the reuptake of three chemical messengers (neurotransmitters), which are norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. These neurotransmitters help regulate mood, norepinephrine impacts mood and energy, and dopamine is involved in memory, motivation, and movement.
Examples of Common SNRIs
There are several SNRIs. They vary based on how they work and what they treat. Some common SNRIs include:
- Cymbalta (duloxetine) and Drizalma Sprinkle (duloxetine), which are used to treat:
- Effexor (venlafaxine) and Effexor XR (venlafaxine), which are taken to manage:
- Major depressive disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Social anxiety disorder
- Fetzima (levomilnacipran), Pristiq (desvenlafaxine), and Khedezla (desvenlafaxine), which are used to treat major depressive disorder
- Savella (milnacipran), which is used to manage fibromyalgia
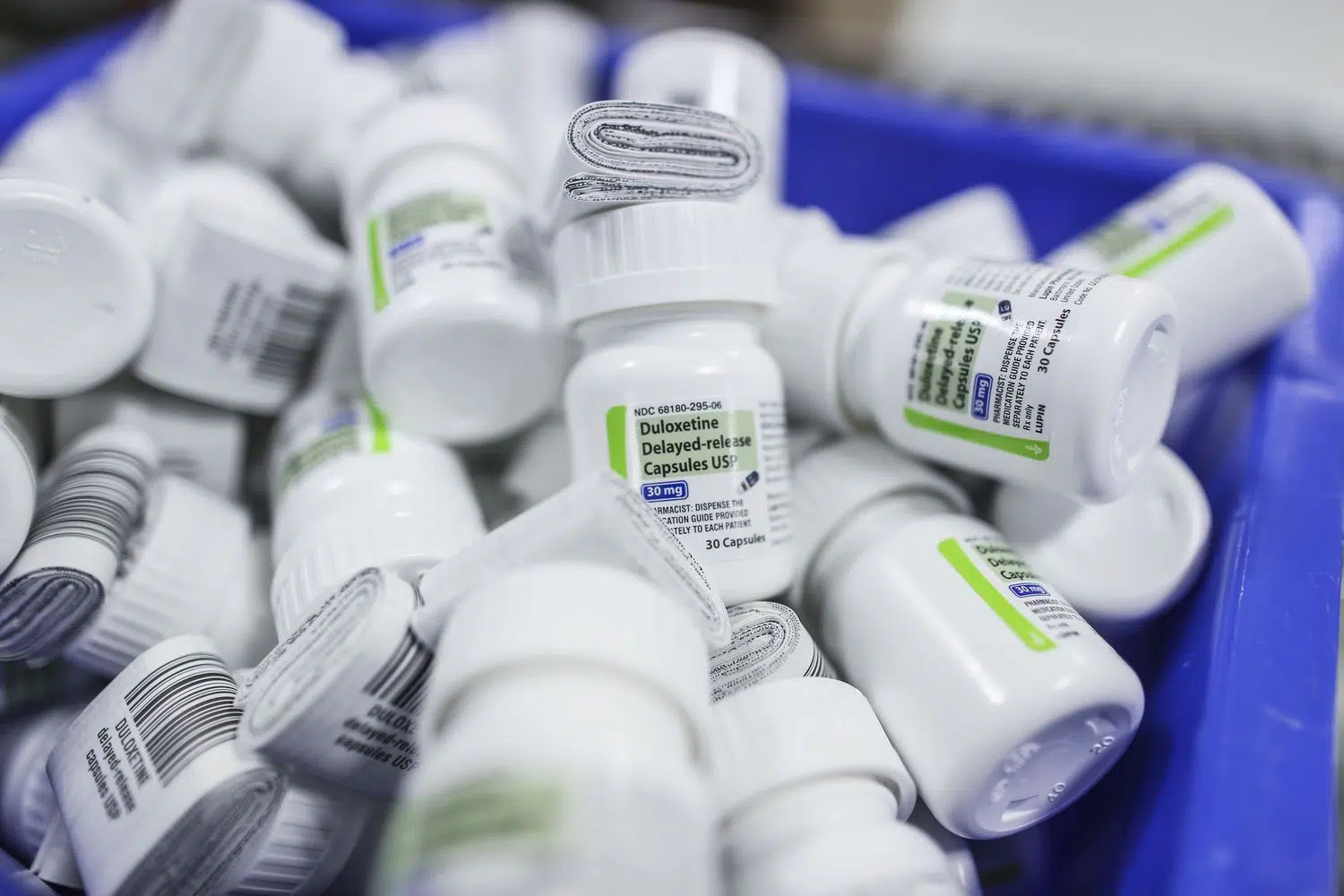
Duloxetine Recall
Starting in October 2024, over 200,000 bottles of duloxetine delayed-release capsules were recalled due to concerns about the presence of nitrosamines, which can increase the risk of cancer. If you take duloxetine, check your medication packaging to see if it was part of the affected lots or call your pharmacist to find out. You should also contact your prescriber, as abruptly stopping a medication like duloxetine can be dangerous.
SNRIs vs. SSRIs: Which Work Better?
SNRIs and SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors) are both antidepressants but work differently. SSRIs work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin, while SNRIs block the uptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. Based on clinical research, SNRIs show superior antidepressant activity to SSRIs, especially in more severe depression.
Drug Interactions
There are a number of drug interactions you should take into consideration as you talk with your doctors about starting on SNRIs. For instance, taking SNRIs with MAOIs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. Therefore, you cannot start MAOIs within seven days of stopping SNRIs. You cannot start SNRIs within 14 days of stopping an MAOI.
Who Should Avoid Taking SNRIs?
There are some cases in which avoiding SNRIs altogether may be best. If you are allergic to your medicine or any of its ingredients, talk to your doctor about other alternatives. If you are taking a MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, you should avoid taking SNRIs.
When to Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
If you are taking SNRIs and have hallucinations, suicidal thoughts, irregular heartbeat, skin blisters or rash, hives, or chest pain, you should consult your healthcare provider about switching to a different treatment.
Summary
SNRIs are a class of antidepressants that can treat depression, anxiety disorders, nerve pain, muscle pain, and fibromyalgia. They work by inhibiting the reuptake of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. SNRIs are more effective than SSRIs in treating severe depression, fibromyalgia, and painful physical symptoms associated with depression. They have fewer side effects and better tolerability than SSRIs, but carry certain risks and precautions, so it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking SNRIs or any other medication.
FAQs
- Q: How do SNRIs work?
A: SNRIs work by inhibiting the reuptake of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine. - Q: What are some common SNRIs?
A: Some common SNRIs include Cymbalta, Effexor, Fetzima, Pristiq, and Khedezla. - Q: Are SNRIs safe?
A: SNRIs can be effective in treating certain conditions, but they may have certain risks and precautions. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking SNRIs or any other medication. - Q: Can I take SNRIs with other medications?
A: There are certain drug interactions you should be aware of when taking SNRIs, such as taking them with MAOIs or other serotonergic drugs.
Recent Posts
HIV vs. AIDS: How They Differ and Why Early Treatment Matters
How HIV and AIDS Differ The main difference between HIV and AIDS is that HIV…
The pandemic badly affected young people’s mental health – but also showed what they need now to thrive
The Teenage Years: A Time of Turmoil and Crisis A New Perspective on Adolescence The…
Taylor Atwood’s Squat Training 4 Weeks out From Powerlifting Nationals
Taylor Atwood on Track for Big Performance Taylor Atwood is considered one of the best…
Are Nicotine Pouches the Best Way to Quit Smoking?
Nicotine Pouches: A New Way to Quit Smoking? Nicotine Replacement Therapy Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT)…
9 TMJ Treatment Options to Release Jaw Tightness
Several Treatments Available to Alleviate Jaw Tightness and Reduce TMJ Flare-Ups 1. Apply Heat or…
Inside Adidas’ Inaugural “Primer” Event: A Fitness Playground for Elite Athletes
Adidas Brings Professional Athlete Treatment to CrossFit with "Primer" Training Camp As the roster of…


